1. Download and installation
Neo4j is a very popular, widely-used No-SQL graph database. Let us first try to download and install neo4j on our own laptop. Go to their official webpages, and try to download it on your own system.Download Center .(I am using Win10 and for learning usage, download Neo4j Community Edition 3.5.5). After download the starting file, let us try to start the server next.
1.1 start the server
open an console and cd to your the install directory of neo4j. run the following command
$ cd <your the install directory of neo4j>
$ bin\neo4j consoleyou will get
INFO ======== Neo4j 3.5.5 ========
INFO Starting...
INFO Bolt enabled on 127.0.0.1:7687.
INFO Started.
Remote interface available at http://localhost:7474/then, goes to your browser and enter http://localhost:7474/. you will see the following web interface.
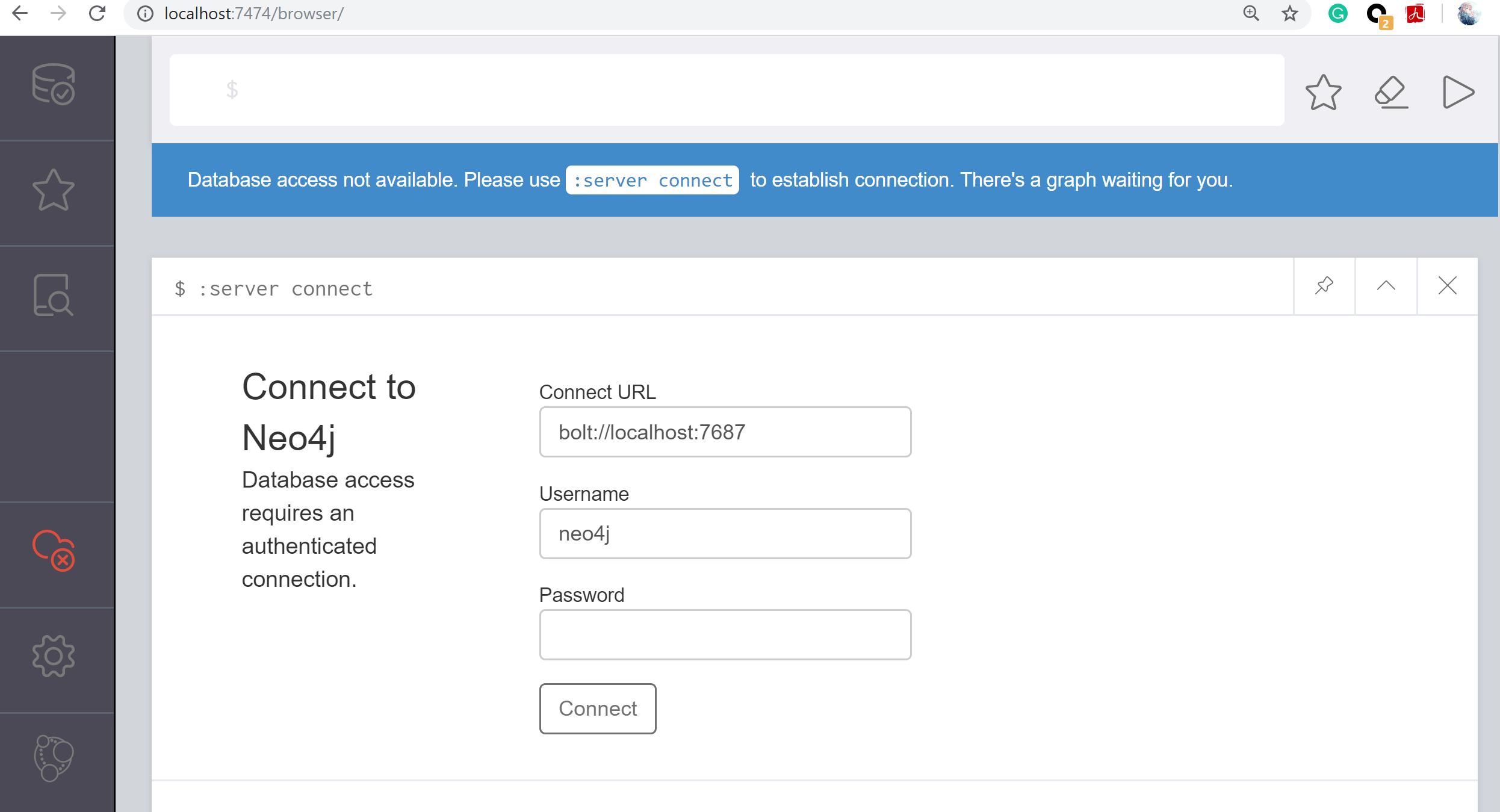
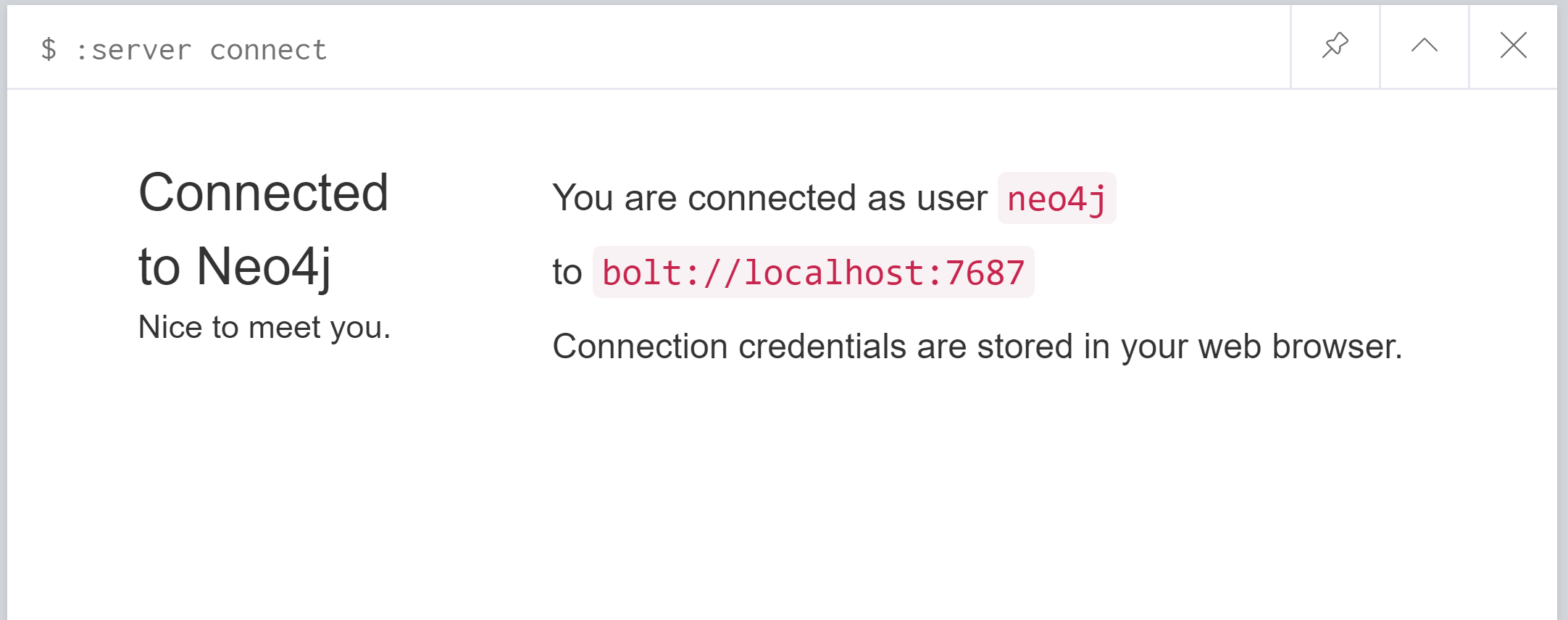
1.2 Authenticated connection to the database.
Connect using the default username ‘neo4j’ with default password ‘neo4j’. It will leading to a instruction for you to set your own password for conection.
Now we are done.
2. Neo4j: Data Model & Architecture
Neo4j uses Native Graph Processing Engineer(GPE) to store the graph. To be specific, data are stored in the form of Nodes and properties related to that data are stored as key-value pairs, where Key is the property name and value is property value. For example, if I have one worker named Kitty and has some properties like, Id, gender ,department etc. So the node looks like the following:
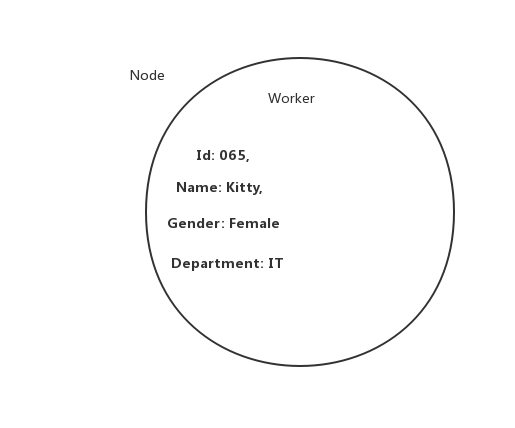
Here, the node has a label called worker. As we known, each work is employee of one company. So, an edge describes the relationship between labels.
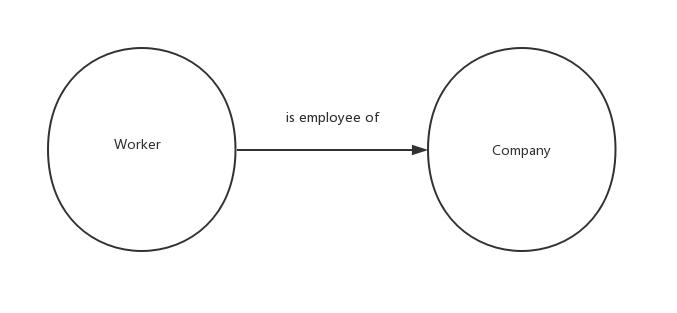
In order to do some manipulations on the database, let us first know about the data type supported in Cypher Query Language (CQL).
2. Cypher Query Language (CQL).
2.1 Creating Single and Multiple Nodes with label
Syntax:
$ Create (Node_Name_1),(Node_Name_2),...Example
$ Create (Student),(School),(Subject)When we creating a node, we could add labels to that node, the syntax is :
Syntax:
$ Create (Node_Name:Node_label)Example
$ Create (Kitty:Worker)To view all the nodes we have created before, using match clause without any conditions to get all results
$ MATCH (n) return nWe can see all the nodes created before, notice that, each node in the graph has its own id, and neo4j automatically generated id for each node.
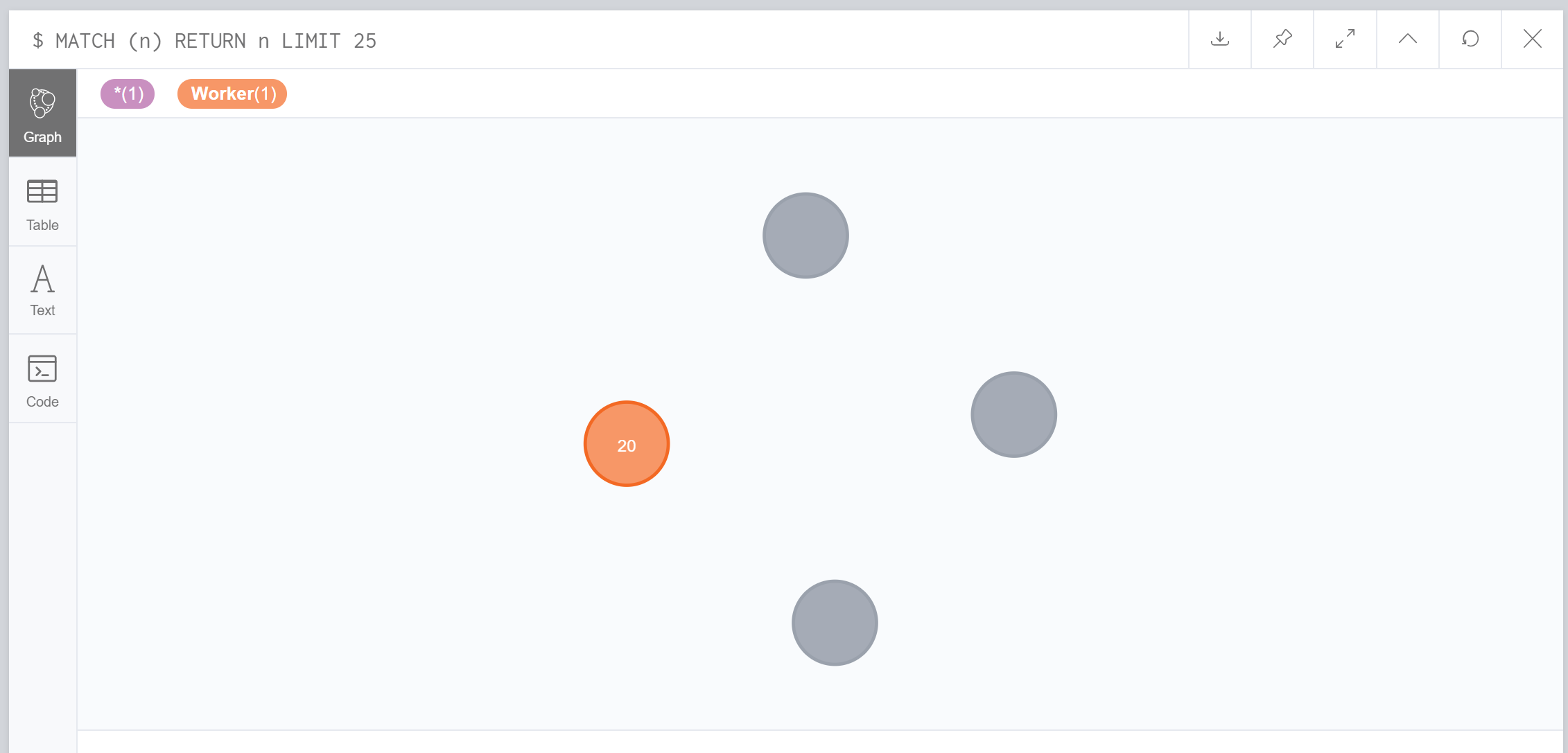
Each node can have not only one labels, but also have multiple labels.
Syntax:
$ Create (Node_Name:Node_label_1:Node_label_2:Node_label_3:...)Example
$ Create (John:Teacher:Student:Professor)2.2 Creating Nodes with properties
As above discussion, nodes are actually key-value pairs,
Syntax:
$ Create (Node_Name:Node_label{<key>:<value>, <key>:<value>, ...})Example
$ Create (Kitty:Worker{Gender:"Female", Department:"IT service"})After run the MATCH CLAUSE, we could see the result.
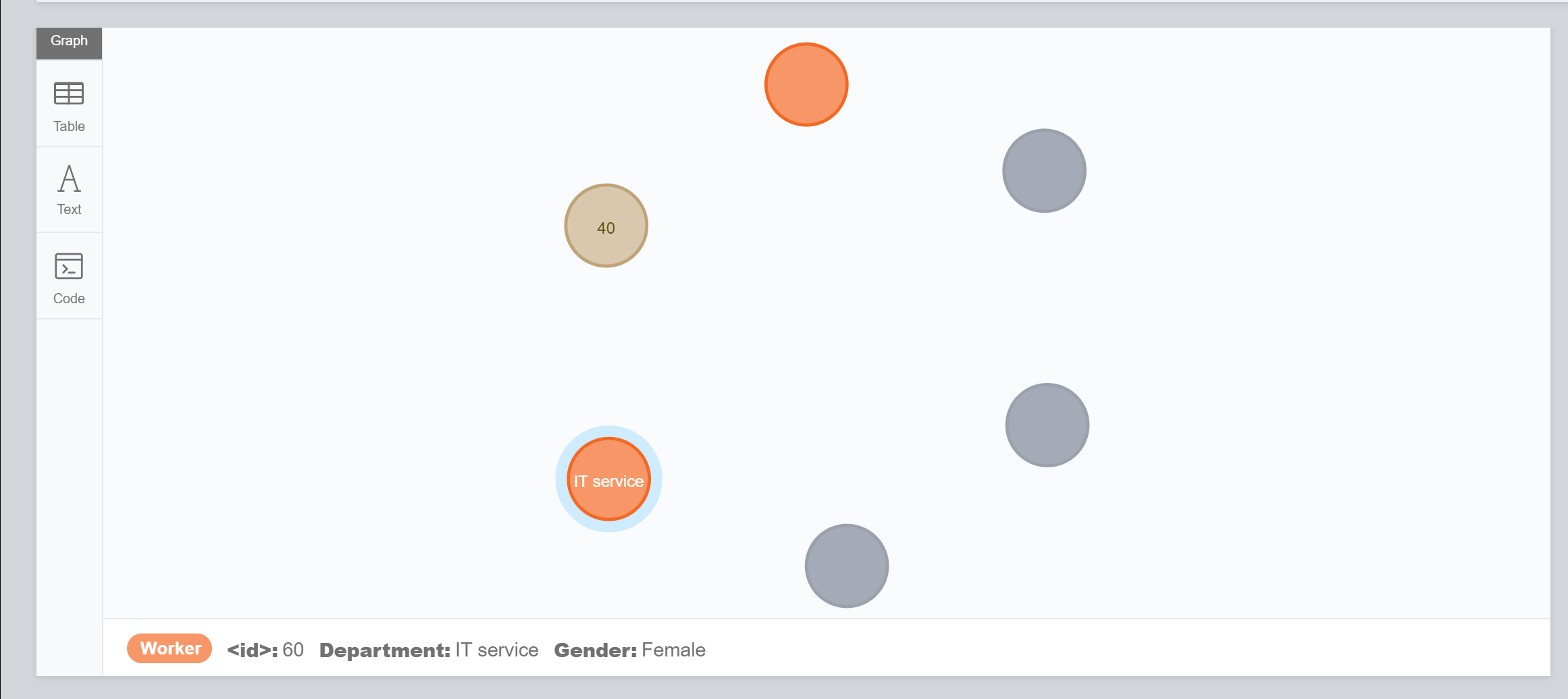
2.3 Creating Nodes with properties
Before we establishing relationship between different nodes, let’s look at how to use where clause.
Syntax:
$ MATCH(node:Node_label) WHERE node.property="some_value" RETURN node;Example : find all the female employees.
$ MATCH (worker:Worker) WHERE worker.Gender = "Female" RETURN worker;2.4 Create Relations between nodes.
Syntax: Create nodes and creating relationships between them
CREATE (node1),(node2),(node3),(node1)-[r:Relation1]-> (node2),(node2) -[r:Relation1]-> (node3)Syntax : Select existing nodes and creating relationships between them.
MATCH(a:Node_label),(b:Node_label) WHERE a.ID = ??? AND b.ID=??? CREATE (b)-[r:R] -> (a)Example:
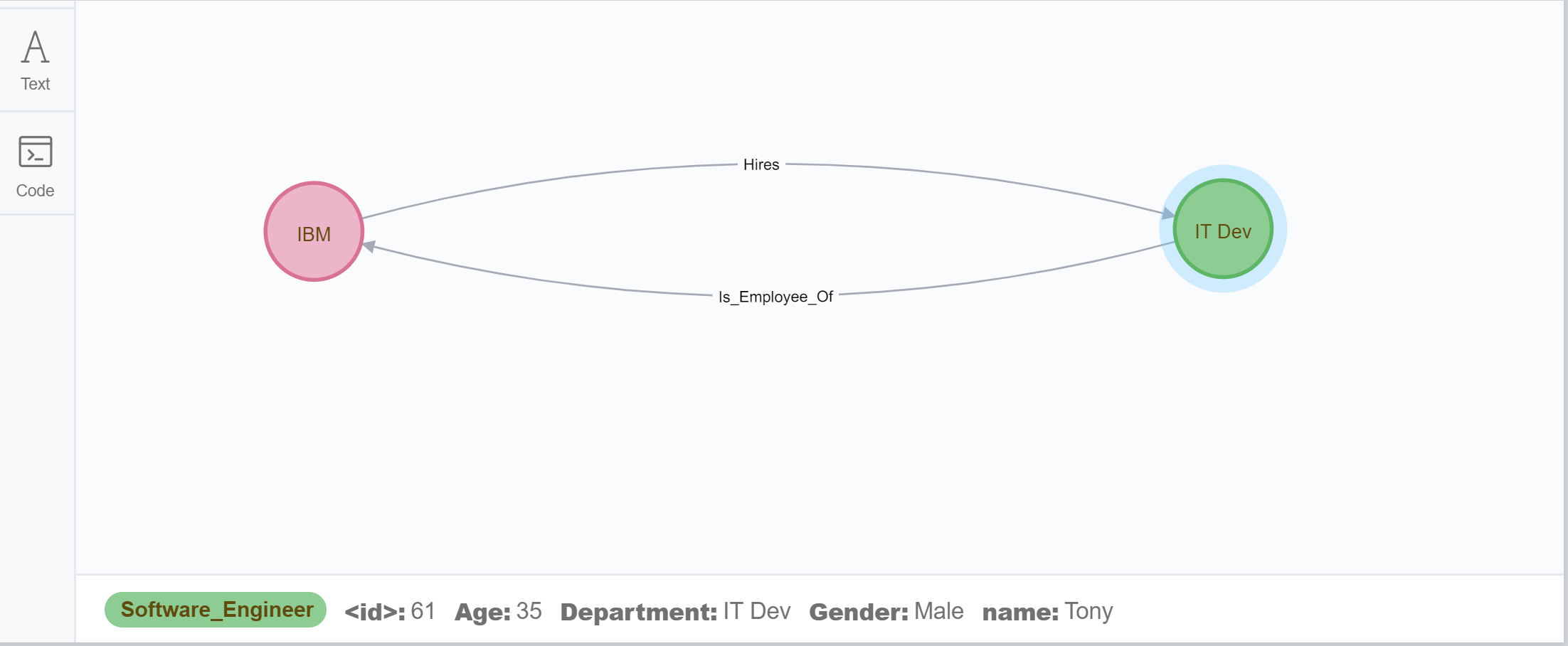
CREATE(Tony:Software_Engineer{name: "Tony", Gender: "Male", Department: "IT Dev", Age: 35}),
(IBM:Company{name:"IBM"}), (Tony)-[r:Is_Employee_Of]->(IBM) RETURN Tony, IBM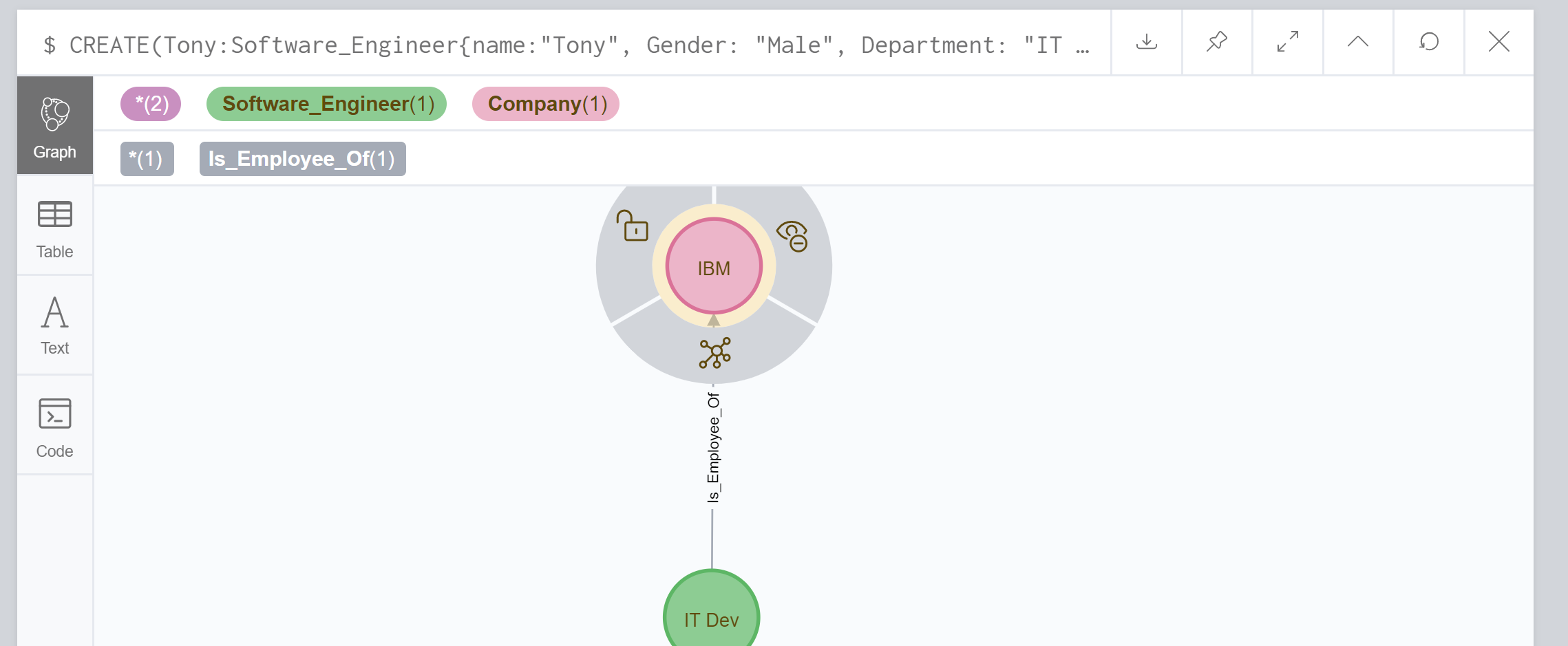
Example: Create relationships between existing nodes.
MATCH(software_eigneer:Software_Engineer),(company:Company) WHERE software_eigneer.name = "Tony" AND company.name="IBM" CREATE (company)-[relation:Hires] -> (software_eigneer) RETURN software_eigneer, companyResults:Java


